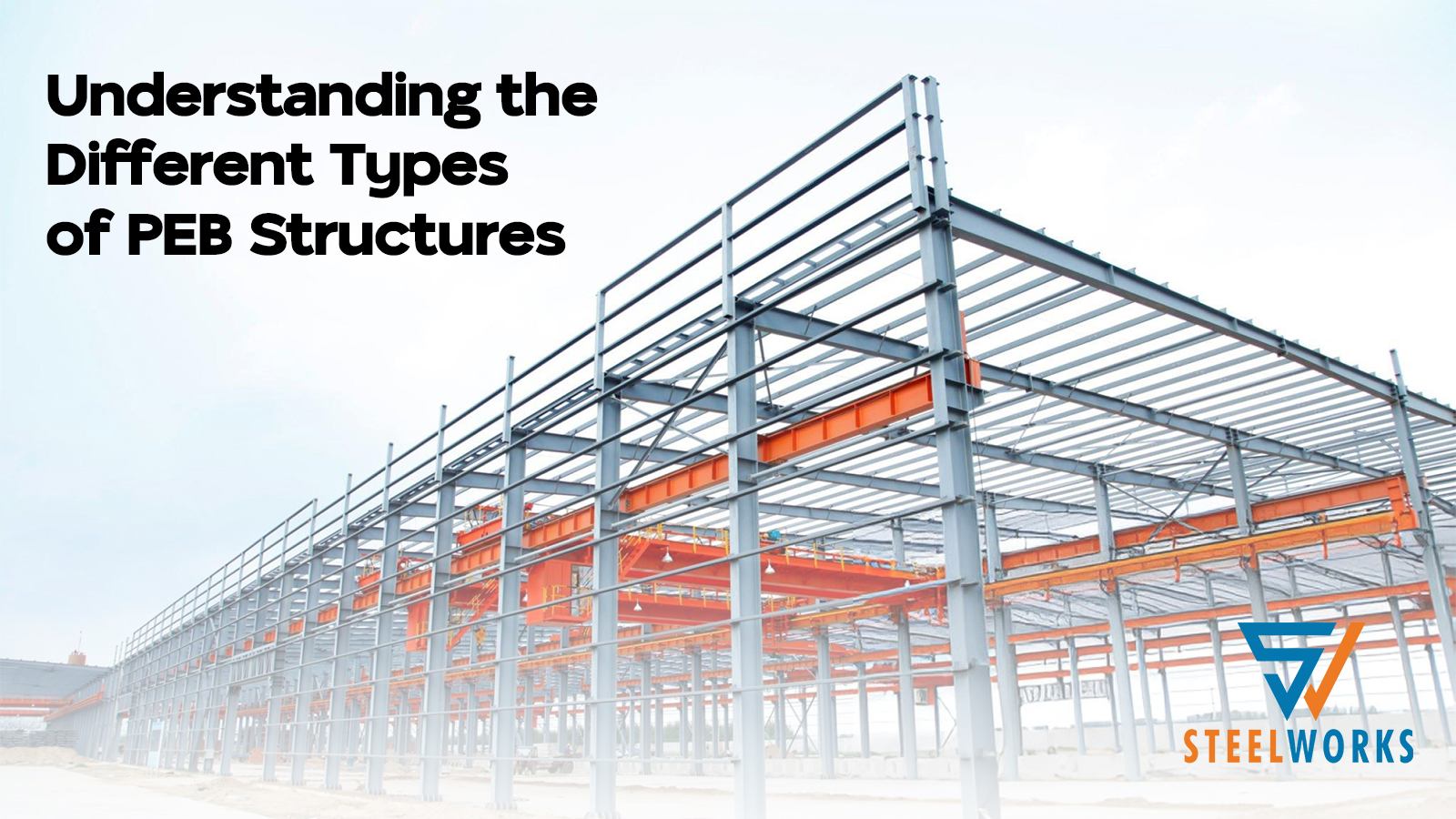
PEB structures are transforming the Indian construction industry and around the world. But what are they, and how do you select the right one for your project? This article will break down everything you need to know in a simple way.
We will cover the different Types of PEB structures, their fundamental elements, and the advantages that make them popular among everyone, from warehouse owners to workshop operators.
What is a Pre-Engineered Building (PEB)?
A Pre-Engineered Building (PEB) is an advanced building system in which parts are fabricated within a factory and subsequently installed on-site. Imagine it like constructing using high-tech Lego blocks every piece is engineered and made to assemble perfectly with others, culminating in a building process that is quicker, more effective, and sometimes more affordable than the traditional ones.
These structures are best suited to low-rise buildings (usually two stories or below) and are extensively applied in industrial, commercial, and institutional construction. The secret to a PEB’s strength and efficiency is its two primary framing systems: the primary structure and the secondary structure.
What is the Primary Structure of PEB?
The primary structure of a PEB is its central backbone or skeleton. It is made to support the entire load of the building, such as the roof, walls, and any other loads like snow, wind, or cranes. This framework is usually composed of high-strength, hot-rolled steel sections and consists of elements such as columns and rafters.
Identifying the primary structure is important as it specifies the shape and size of the building. The various Types of PEB structures are defined mostly based on their primary frame designs.
Exploring the Different Types of PEB Structures
Choosing the right frame type is essential for optimizing space, cost, and functionality. Here are the most common Types of PEB structures available in the market .
The table below gives a quick overview of the primary options:
| PEB Structure Type | Ideal Span Range | Key Features & Best Use Cases |
| Clear Span | Up to 150 meters | These are unobstructed internal spaces; ideal for aircraft hangars, big warehouses, and sports stadiums. |
| Multi-Span | 50+ meters | Employing internal columns for larger buildings is a budget-friendly option for industrial buildings and large factories. |
| Single Slope | 15-30 meters | Sloping roof in one direction; typically employed for small warehouses, retail units, and building extensions. |
| Multi-Gable | 50-120 meters | Has multiple roof peaks; it provides architectural beauty and structural integrity to showrooms and recreational centers. |
| Lean-To | 6-18 meters | An addition to a pre-existing building, suited for the addition of workshops, storage, or covered parking. |
| Hybrid | Varies | Combines PEB systems with traditional construction (e.g., concrete); used for projects with unique architectural needs. |
Types of Insulation in PEB Structure
The important factors in constructing comfort and energy efficiency is understanding the Types of insulation in PEB structures. Ideal insulation ensures temperature regulation, condensation reduction, and noise reduction.
- Fiberglass Blanket Insulation: The most widely used option for PEBs, owing to its rapid installation and affordability. It also has good fire retardancy and sound resistance.
- Rigid Board Insulation: It is constructed using foam boards and is very thermally efficient and vapor-retardant. It is possibly more costly but results in superb energy efficiency.
- Spray Foam Insulation: This type of insulation is sprayed on as a liquid that then expands into foam and forms a great air barrier and has a high R-value (a measure of thermal resistance).
Choosing the appropriate insulation is a function of your local climate and the use of the building, dramatically influencing long-term energy expenditures .
The Top Benefits of Choosing a PEB
The different Types of PEB buildings have certain important benefits compared to conventional construction techniques.
- Cost-Effectiveness: PEBs can save overall construction expenses by as much as 30%. These cost savings result from optimizing material utilization, lower labor expenses due to accelerated assembly, and shorter project durations.
- Fast Construction: As pieces are pre-designed and made off-site, assembly on-site is extremely fast, saving a lot of time. Projects can be finished in half the time of traditional buildings.
- Design Versatility & Endurance: These pre-engineered structures are highly flexible in design and may be adapted to suit particular architectural requirements. Constructed from high-strength steel, they are long-lasting and can endure severe climatic conditions.
- Low Maintenance and Sustainability: Steel structures have a resistance to rust and corrosion, and they need little maintenance during their long lifetime. In addition, steel can be recycled, which makes PEBs an eco-friendly option.
Conclusion
From big and column-free plane hangars (Clear Span) to productive factory floors (Multi-Span) and functional building extensions (Lean-To), the various Types of PEB structures provide a clever, efficient, and multifunctional solution for contemporary construction requirements.
Knowing the primary structure of a PEB and the types of frames gives you the power to make an educated choice for your next project. As the construction industry keeps on developing, these advanced building systems are opening doors to a future where development will be quicker, more economical, and sustainable.